Diversity of rocks and the erosion in a steep sector of Âncora river
Ferida Má Cascades are located in Âncora river. The high slope early section of the waterfall is cut into the granite. After, the river crosses dozens of schist and quartzite layers with a different resistance to erosion (esq. A).
The alternation of rocks with different erosional strength gives rise to steps sometimes higher than 5 m (esq. B).
The most popular falls are also known as Pincho cascade, located along a succession of quartzitic layers.
At the cascades, erosion acts in particular at the top and bottom of the waterfall. At the top, the erosive action of the running water might lead to a retreat of the waterfall edge and the formation of rapids. At the bottom of the waterfall, the erosion caused by the falling water excavates "pits" that can originate small lakes (esq. C).
Ferida Má waterfalls are essentially due to lithological aspects related to the erosion resistance of
metamorphic beds, as well as their orientation. However, the shape and slope of the riverbed were also
influenced by sea level changes and tectonic uplift. The continuous increase in the difference of altitudes
between the mouth and the river source, due to sea level fall to continuing tectonic uplift of the continent
were a decisive factor in revitalizing the river erosion in the search for a new equilibrium profile (Fig. 1).
References:
Pereira, P; Henriques, R.; Brilha, J. & Pereira, D.I. (2019). Conteúdos científicos para a caracterização dos 8 monumentos naturais locais” enquadrado no projeto Geoparque Litoral de Viana do Castelo – 2ª fase. Município de Viana do Castelo, Relatório Final GEOSITE, 273 p.
Ferida Má Cascades are located in Âncora river. The high slope early section of the waterfall is cut into the granite. After, the river crosses dozens of schist and quartzite layers with a different resistance to erosion (esq. A).
The alternation of rocks with different erosional strength gives rise to steps sometimes higher than 5 m (esq. B).
The most popular falls are also known as Pincho cascade, located along a succession of quartzitic layers.
At the cascades, erosion acts in particular at the top and bottom of the waterfall. At the top, the erosive action of the running water might lead to a retreat of the waterfall edge and the formation of rapids. At the bottom of the waterfall, the erosion caused by the falling water excavates "pits" that can originate small lakes (esq. C).
Ferida Má waterfalls are essentially due to lithological aspects related to the erosion resistance of
metamorphic beds, as well as their orientation. However, the shape and slope of the riverbed were also
influenced by sea level changes and tectonic uplift. The continuous increase in the difference of altitudes
between the mouth and the river source, due to sea level fall to continuing tectonic uplift of the continent
were a decisive factor in revitalizing the river erosion in the search for a new equilibrium profile (Fig. 1).
References:
Pereira, P; Henriques, R.; Brilha, J. & Pereira, D.I. (2019). Conteúdos científicos para a caracterização dos 8 monumentos naturais locais” enquadrado no projeto Geoparque Litoral de Viana do Castelo – 2ª fase. Município de Viana do Castelo, Relatório Final GEOSITE, 273 p.
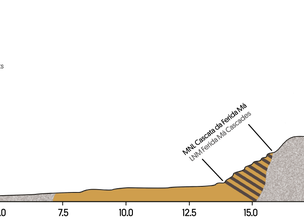
Esq. A - Âncora river profile and location of Ferida Má cascades.
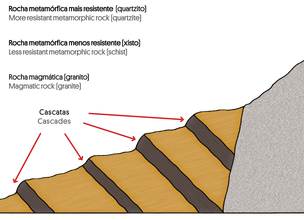
Esq. B - Ferida Má Cascades profile.
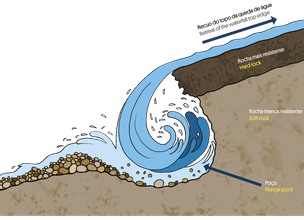
Esq. C - In cascades, erosion acts in particular at the top and bottom of the waterfall.
Location
Montaria
Coordinates
Lat: 41.79726544186158
Long: -8.753917688447352
Hello little one!
I'm Piquinhos and I can help you learn more about the Geopark!
Technical details
Esq. A - Âncora river profile and location of Ferida Má cascades.
Esq. B - Ferida Má Cascades profile.
Esq. C - In cascades, erosion acts in particular at the top and bottom of the waterfall.
Child Mode
Discover the geopark in a simpler format, aimed at the little ones.
Clique ENTER para pesquisar ou ESC para sair
